Gabriele Stoll
Natural Crop Protection in the Tropics
Letting Information Come to Life
Methods of Field Protection
Insects
Insect-controlling plants
Annona
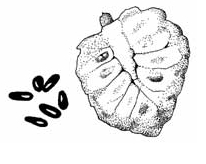
Sweetsop (Annona squamosa)
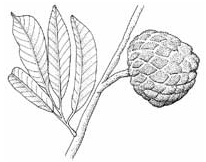
Soursop
(Annona muricata)
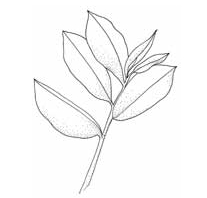
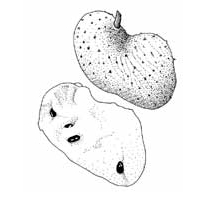
Custard apple
(Annona reticulata)
Fam. Annonaceae
Sweetsop
Soursop
General
More than 90 species of small trees and
shrubs are known in the Annonaceae family. They occur mostly in
tropical America, but some are also found in Asia and Africa.
Soursop and custard apple are widely distributed in Central
America and the Caribbean, while sweetsop is commonest in India
and Southeast Asia. They do not require special conditions of
soil or water, but thrive best in places where there is a clear
division between the rainy and dry season, and generally prefer
dry sites. The effective ingredients are found in the unripe
fruit, and in the seeds, leaves and roots. The oil content of
the seeds amounts to 42–45%. On ordinary soils, the yield
ranges from 50 to 100 fruits per tree, in fertile soils it may
reach up to 500. A well maintained orchard can be economical
for 15–20 years.
Plant parts with insect-controlling
properties
Seeds, leaves, unripe fruits
Mode of action
Contact and stomach poison
Ovicidal, insecticidal, repellent,
antifeedant, antinematode/nematocidal
Target pests
Field insects
Aphids
Brown rice planthopper
Caterpillars
Chrysanthemum aphid
Coffeegreen scale
Cotton stainer
Diamondback moth
Green bugs
Green rice leafhopper
Mediterranean fruitfly
Oriental fruitfly
Potato aphid
Red pumpkin beetle
Southern armyworm
White-backed rice planthopper
general
Nilaparvata lugens
general
Macrosiphoniella sanborni
Coccus viridis
Dysdercus koenigii
Plutella xylostella
general
Nephotettix virescens
Ceratitis capitata
Bactrocera dorsalis
Macrosiphum euphorbiae
Aulacophora foveicollis
Spodoptera eridania
Sogatella furcifera
Side effects on humans
When handling the seeds of Annona, care
should be taken to ensure that the powder does not come into
contact with the eyes, as this causes painful irritations.
Special characteristics
The seeds are much more toxic than the
leaves.
Methods of preparation and use
Custard apple leaf extract
500 g of custard apple leaves are boiled
in 1–2 litres of water. Allow to boil down to ca. 1/4 of
the original liquid. Strain this liquid and mix it with
10–15 litres of water. This is ready to be sprayed over
the crop. For one hectare, 5–7.5 kg of fresh leaves are
required.
Custard apple – calotropis –
tobacco extract
Take 500 grams of custard apple leaves and
boil in 1–2 litres of water. Allow to boil until it
becomes thick. Filter the solution to receive the decoction.
Take 250 to 300 ml of calotropis extract made from the leaves.
Take 500 g of tobacco leaves and boil in 1–2 litres of
water for ca. 45 minutes. Then filter the extract and add 250
ml of biogas waste (whitish fluid which deposits in the biogas
digester) and 100 g of copper sulphate. Mix the above
ingredients with 60 litres of water and spray over the crop.
The above quantity is recommended for 0.4 ha.
Custard apple – neem – chilli
extract
Take 2 kg of custard apple leaves and
grind them well. Add 500 ml of water and stir. Filter to get
the extract. The filtrate is kept aside. Take 500 g of dried
chillies and soak them in water overnight. Next day, grind and
filter the solution to get the extract. Take 1 kg of crushed
neem fruits and soak in 2 litres of water overnight. Then
filter the extract. Mix all the three filtrates with
50–60 litres of water. Filter again and spray over the
crops.
Custard apple seed extract
Use this solution to spray plants infested
with aphids or ants. Crush seeds of custard apple and mix them
with water at a rate of 40 g per litre. From Thailand farmers
reported that they prepare a spray made of 500 g finely ground
seeds which are soaked in 20 litres of water for 1–2
days. After filtering it is ready to be sprayed. This spray is
claimed to be highly effective.
Other uses of plant or substance
• Leaves are medicinal for a number
of ailments.
• Fresh flowers are eaten as food.
The wood is not attacked by white ants. In India it is often
used for carts and house construction.